Setup
- Test site for all skills transfer practice: https://pvu-test.performx.com.au/
- Login: https://pvu-test.performx.com.au/user/login
- Site with prototype content loaded, to use for comparison: https://power-vu.performx.com.au/
- Information Architecture for prototype content, developed from Site and Space: Site and Space IA.xlsx
- Design document for content types used in distribution, which may provide context if anything is confusing: Content Type Design.xlsx
- Drupal User Guide, for understanding basic processes: https://www.drupal.org/docs/user_guide/en/index.html
Basic structure
Adding content
Please see the Drupal User Guide for detailed steps about adding content. In this document we’ll just discuss some things which are unique to this distribution.
Most content on your websites will be classed as ‘Content’, with some ‘Media’. You won’t really be using ‘Blocks’.
Content types
There are 6 content types in this distribution. Five of them were designed with reference to ‘types’ from schema.org, in close consultation with the Power team. This design, using structured data, enables the distribution to be applied broadly.
- Basic page - Use for your static site content, such as an 'About us' page.
- Event - Use for events. Events include a ‘Part Of’ field so that you can make an Event a part of another Event, such as a Festival or Program.
RDFS Class: schema:Event URI: https://schema.org/Event - Item - Usefor most pieces of content. This content type is intentionally broad so it can be used for many kinds of content, even within a single website. ‘CreativeWork’ is the schema.org type that was used as the basis for this content type, which might help you imagine the kinds of content an Item can encompass.
RDFS Class: schema:CreativeWork URI: https://schema.org/CreativeWork - Person - Use for people, e.g. project members, authors, contributors, etc.
RDFS Class: schema:Person URI: https://schema.org/Person - Place - Use for places. Typically you will need to add Places because they are referenced in other content types.
RDFS Class: schema:Place URI: https://schema.org/Place - Project - Use for pieces of content that are larger than an Item. This typically means they will encompass other pieces of content. ‘Collection’ is the schema.org type that was used as the basis for this content type, which might help you frame what to use Projects for.
RDFS Class: schema:Collection URI: https://schema.org/Collection
Edit content types
To edit these content types, go to Structure > Content Types. You can change their names if you would like them to be more or less specific for a particular use case. You can also edit, add, or delete their fields.
Keep in mind that any changes you make will only apply to the current Drupal site that you’re working on: the base content types for the distribution will always be the same when you provision a new site. If you want to change the base content types, please discuss that with us.
Taxonomies
There are a handful of taxonomies used in fields across the distribution. Some already include predefined terms, many of which are sourced from schema.org or other formal vocabulary sources, about which the Power team was consulted. You can add terms to these to any extent you wish. Others have no predefined terms, and will need to have terms added on a site-by-site basis.
- Custom Keywords - No predefined terms. The inclusion of this field, alongside the standard ‘Keywords’ field, was to provide a ‘clearing house’ for keyword terms that are not included in standard vocabularies.
- Event Status - Predefined terms.
- Event Type - Predefined terms.
- Item Status - Predefined terms.
- Item Type - Predefined terms.
- Keywords - No predefined terms. The inclusion of this field, alongside the ‘Custom Keywords’ field, was to act as a repository for keywords sourced from a single formal taxonomy chosen by you, e.g. the LOC Subject Headings. These need to be selected and added.
- Language - Predefined terms.
- Material - Predefined terms.
- Role - Predefined terms.
- Tags - No predefined terms. This is a built-in Drupal taxonomy. I think you will primarily use this field as an internal tool to group content within Views. In most cases, to categorise content for the user’s benefit we recommend using ‘Keywords’ and ‘Custom Keywords’.
Edit taxonomies
To edit these taxonomies, including by adding terms, go to Structure > Taxonomy.
You can add as many terms as you wish. You should always double-check the existing terms to make sure you don’t accidentally add a duplicate term, either conceptually or through spelling error. Except for in the ‘Keywords’ taxonomy, you don’t need to worry about sourcing keywords from within an existing formal taxonomy.
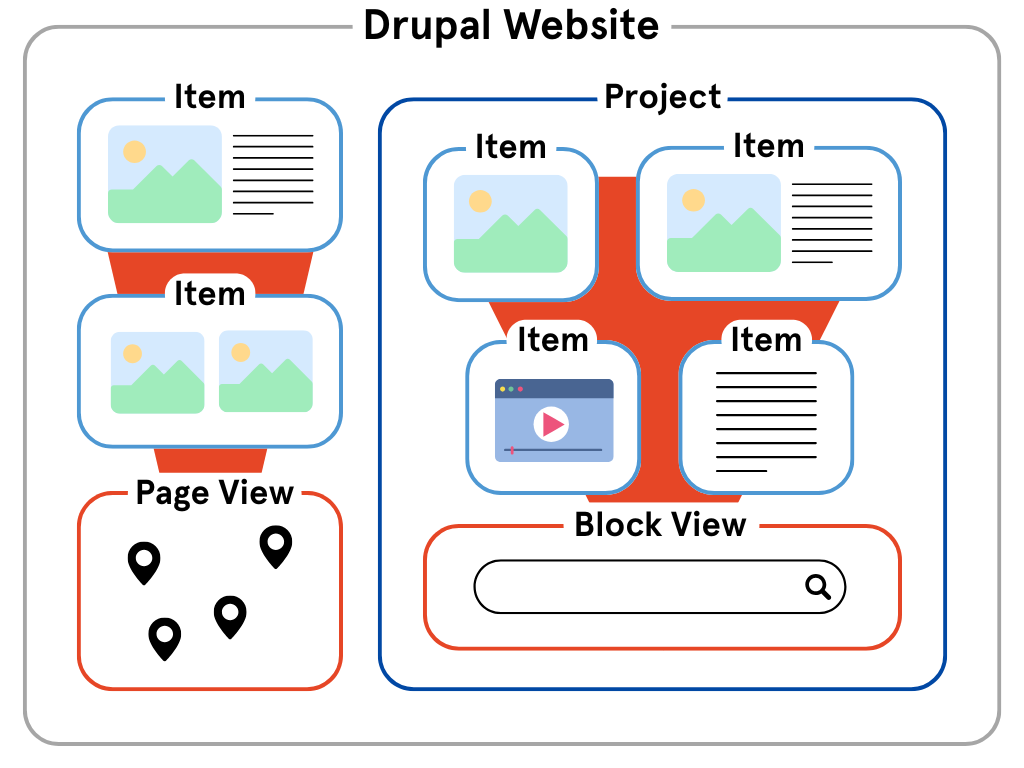
Views
In Drupal, a View is a way of listing content on a website. You will probably use them a fair amount on your websites to group content in a certain way; for example, to make a page that lists all Events after a certain date.
Page Views
Most Views constitute an entire page in the website. Our distribution comes with several of these Page Views already built in. For example, the Index, Map, and Node Graph pages are Views. There are also more simple Views that render as ‘listing’ pages: we have built in a listing page for most custom content types (Events, Items, People, and Projects).
To edit any of these views or create your own, go to Structure > Views.
There are a lot of ways you can customise a View, including changing the format, showing or hiding certain fields, and filtering content shown based on detailed criteria. Check the Drupal User Guide for in-depth documentation of all the possible settings.
Block views (e.g. searches on Project pages)
There may be cases where you want to embed a View within an existing page, rather than have it take up an entire page. For example, a common use case might be to add a View to the bottom of a Project page that allows users to search all Items that have been listed as ‘Part of’ that Project. In those cases, you would create a Block View.
The process of creating a Block View is the same as creating a Page View (i.e. you can easily do it by going to Structure > Views). However, to show a view on a page you need to add it as a block to the layout of a page. You do this in Structure > Block layout. Usually, you would place the block in the Content section. Once you have placed the block you can Configure it to only show on certain pages or content types.
Theming
We have installed the ‘Power Visual Understanding’ theme for this distribution. You can make small changes to the theme’s settings, like changing the logo and the favicon, in Appearance > Settings > Power Visual Understanding. If you would like to make major changes to the theme, either for the entire distribution or on a particular website, please let us know and we can undertake a design process with you.